A CO2 laser is a type of gas laser. It is very robust and reliable and relatively easy to build. It was really among the earliest kinds of lasers to be constructed in 1964. The laser medium for this type of laser usually consists of a mixture of CO2, nitrogen, and helium. CO2 lasers belong to the class of high-power lasers. The radiation that is emitted by such lasers lies between 9.4 and 10.6 µm. They are able to reach output powers of tens of kW and output energies of up to 100 J. They are widely used in a variety of sectors since they are able to provide such high outputs. CO2 lasers of up to 200 W of output power are typically used for laser cutting and engraving of various materials, including plastics and wood. Pulsed lasers with up to 6 kW output power are used for cutting or engraving ceramics or thick metal plates (several cm thicknesses).
The laser is able to be used for welding, hardening, or melting bulk materials if the output power is more than 6 kW. One extremely important field for CO2 lasers is medical surgery on soft tissue. This is because water and, thus, skin or flesh absorb infrared laser radiation very well. Hence, CO2 lasers are able to be used for surgical cutting or hemostasis (i. e. stop bleeding). The most common fields of medical applications are cosmetic surgery, dentistry, and gynecology. Other industrial uses include areas such as automotive, aerospace, or the defense industry.
Who invented the CO2 Laser?
The CO2 laser was invented in 1964 by Kumar Partel. Partel was an electrical engineer at the AT&T Bell Labs at the time. Physicists spent a lot of time studying lasers during those years even though they had no practical uses. The first lasers were used for material processing in the late 1960s. It took another 20 years until CO2 lasers were successfully applied in medicine, primarily for aesthetic surgery.
Prof. Partel was awarded several prestigious science prizes, the latest being the National Medal of Science in 1996.
How does a CO2 Laser Work?
A CO2 laser mainly consists of a sealed tube, which contains up to 20 % CO2, the same amount of nitrogen, and some hydrogen or xenon along with helium. The tube itself has to be cooled either with water or air. The laser light is created by turning the gas mixture inside the tube into plasma. This is done very often by using an electric discharge. First, the nitrogen molecules get electronically excited and transfer some of their energy to the electrons in the CO2 molecules. The carbon dioxide particles relax into a state of lesser energy after a brief period of time, and they then emit normal laser light. This radiation has a wavelength of some microns.
There are two suitable mirrors on both ends of the tube. One is a nearly perfect mirror that reflects laser radiation. The other one lets some fraction of the radiation through. The laser light is linked out using this method and able to be applied where it is needed.
What are the uses of CO2 Lasers?
Listed below are the uses of CO2 lasers.
- Cutting: A variety of materials, such as textiles, metals, wood, and polymers, may be cut with CO2 lasers. They are perfect for production and prototyping because they can make accurate, clean cuts.
- Welding: Metals, polymers, and other materials are able to be welded using CO2 lasers. They generate a focused beam of energy that is able to melt and fuse materials, forming solid, long-lasting connections.
- Engraving: Wood, acrylic, glass, and stone are just a few of the materials that are able to be engraved using CO2 lasers. They are perfect for developing distinctive and bespoke items since they are able to produce detailed patterns and unique logos.
- Laser sintering: A laser is used to melt and fuse powdered materials together to form 3D things. CO2 lasers are able to be utilized for this operation. Prototyping and additive manufacturing both often employ this method.
- LIDAR Systems: LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) systems employ laser pulses to measure distances and produce three-dimensional (3D) maps of surroundings. CO2 lasers are able to be used in LIDAR systems. LIDAR systems are often used in surveying, autonomous driving, and robotics.
- Microfluidics (for drilling µm holes in common plastics such as PMMA): PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate), which is often used in microfluidics devices, is able to be drilled with CO2 lasers at the microscale. The lasers are able to create accurate, clean holes with widths in the micrometer range.
- Soft tissue surgery: CO2 lasers are able to be used to cut, cauterize, and evaporate tissue during soft tissue surgery. They generate a focused beam of energy that is able to target tissue accurately and eliminate it without harming nearby tissue. Dermatology, obstetrics, and oral surgery all often use CO2 lasers.
The last point is the most important because the infrared radiation of 10.6 µm is perfectly absorbed in water. The CO2 laser is used in medicine extremely well since water makes up the majority of human bodily tissue. The most essential usages are cutting tissue and sealing blood vessels.
What are the risks of using CO2 Lasers?
Listed below are the risks of using CO2 Lasers.
- Fire hazard: CO2 lasers generate great heat, which is able to start fires if not utilized correctly. It is essential to observe all safety measures and avoid using the laser near combustible items.
- Skin and tissue damage: Burns and tissue damage are able to result from CO2 laser usage if the laser beam is directed toward the skin or other tissues. Appropriate safety precautions must be used, such as wearing protective gear and avoiding direct exposure.
- Eye damage: CO2 lasers are able to cause significant eye damage, including blindness, if suitable eye protection is not applied. Laser light, whether direct or reflected, is able to permanently damage the retina. Hence proper eye protection is required.
- Electrical shock: It is possible if the CO2 lasers are not properly grounded or maintained since they need high voltages to function.
- Toxic fumes: It is able to be produced by CO2 lasers when they are used to cut or etch certain materials. Working with these materials requires adequate ventilation and respiratory protection.
The most serious danger posed by CO2 lasers is eye damage. Using the proper eye protection is essential at all times while operating a CO2 laser because direct or reflected laser light is able to result in irreversible eye damage or blindness. Other dangers, including fire hazards and skin damage, must be minimized by proper training and safety practices.
What are the advantages of using CO2 Lasers?
Listed below are the advantages of using CO2 Lasers.
- Precision: CO2 lasers are capable of producing very accurate cuts and engravings with high levels of precision and reproducibility.
- Flexibility: CO2 lasers are versatile enough to cut and engrave complicated forms and patterns, making them perfect for prototyping and customizing.
- Versatility: CO2 lasers are flexible instruments for a variety of applications since they are able to cut, weld, engrave, and sinter a broad range of materials.
- Minimal waste: CO2 lasers generate extremely little waste since they remove material via evaporation rather than physical removal.
- Non-contact cutting: CO2 lasers cut materials without contacting them, reducing the danger of damage and the requirement for maintenance.
- Clean cuts: CO2 lasers make clean, accurate cuts with no burrs or other waste, reducing the need for post-processing.
- Speed: CO2 lasers are fast at cutting and engraving materials, making them perfect for high-volume manufacturing runs.
- No tool wear: CO2 lasers do not need physical cutting tools, which removes the need for tool maintenance and replacement.
Precision is possibly the most important advantage of utilizing CO2 lasers out of all of these benefits. CO2 lasers are a crucial tool for manufacturing, prototyping, and other precision applications due to their ability to create exact cuts and engravings with high levels of accuracy and reproducibility.
What are the types of CO2 Lasers?
CO2 lasers are able to be classified in a lot of ways. One is able to divide them into pulsed or continuous wave (CW) lasers. They are able to be ordered according to their output power or to some other parameters.
Listed below are the two types of CO2.
- Ablative CO2 Laser: High-powered ablative CO2 lasers peel skin. They use a precise beam of light to vaporize the top layer of skin, generating new, healthier skin cells. Ablative CO2 lasers repair wrinkles, scars, and sun damage.
- Fractional CO2 Laser: Newer fractional CO2 lasers resurface skin fractionally. It creates tiny regions of damage by sending microbeams deep into the skin. It activates the body’s natural healing reaction, causing new collagen and elastin fibers to enhance skin texture and decrease fine lines and wrinkles. It recovers in a few days, unlike ablative ones. Optimal outcomes may need numerous treatments.
1. Ablative CO2 Laser
The ablative CO2 was the first one, which was used in dermatology. Laser ablation describes the removal of surface material by an energetic laser beam. The technique in medicine is used to remove unwanted tissue, for example, from the skin. This method was first described by Gholam A. Peyman in 1980 when Peyman was working at the Illinois Eye and Ear Infirmary.
2. Fractional CO2 Laser
A fractional CO2 laser is an improvement of the ablative laser. Fractional laser treatment removes only fractions of the tissue. Thus, the hazard of tissue damage is significantly reduced, and the treatment becomes much milder. Hence, this type of laser technology is often used in dermatology for the treatment of wrinkles or acne.
Why is the CO2 Laser the highest-power laser?
A CO2 laser achieves high output power mainly due to its high efficiency, up 20% (as can be read in this book). Another aspect is that the excitation of the laser-active material (i.e., the CO2/N2/noble gas mixture) is very efficient. This means that a significant fraction of the pumping energy is converted into laser energy. Last but not least, exciting a gas mixture has weaker limitations than a solid-state laser. This means the gas in a CO2 laser is able to absorb much more pumping power without damage. A solid-state laser material is going to get burned, melt, or evaporate when too much pumping power is applied. This is no issue for a gas laser, and if the laser is able to be pumped with more energy, the laser beam is going to be more powerful.
What does Continuous Wave Laser mean?
A continuous wave (CW) laser is a kind of laser that continuously produces a beam of light with a fixed amount of power. The laser emits continuous light rather than pulses. A CW laser’s output power is able to change depending on the application and architecture of the laser, although it typically stays consistent over time.
CW lasers are often used in a variety of scientific, industrial, and medical settings, including spectroscopy, laser surgery, and material processing. They are often favored over pulsed lasers in applications that demand a constant, unbroken beam of light.
Continuous Laser Wave is usually simpler and easier to use than pulsed lasers, which produce light in brief bursts. Moreover, they often have lower peak powers, which is beneficial in situations where large peak energies are able to harm the substance being processed or result in undesirable side effects.
What is the wavelength of a CO2 Laser?
The typical CO2 laser has a wavelength somewhere between 9.4 and 10.6 µm. The term “wavelength” in relation to laser technology describes the color of the laser’s light. A laser’s wavelength determines how it interacts with various materials and how effective it is for a particular purpose. Some key factors that are essential to consider when working with CO2 laser are the Beam quality factor (M²), pulse duration, repetition rate, polarization, and power density.
The Beam Quality Factor (M2) measures the laser beam’s ability to concentrate. A more tightly concentrated beam is indicated by a lower M2 number, which is able to be advantageous for specific tasks like cutting and engraving.
The time the laser is on for each pulse is referred to as the “pulse duration.” A shorter pulse duration is able to provide superior results in certain situations.
The repetition rate is the number of laser pulses fired per second. Processing times are able to be accelerated by a greater repetition rate.
The polarization of CO2 laser light is able to be either linear or circular. The processing material’s polarization is able to have an impact on how the laser interacts with it.
Power density is the ratio of laser power to the material being treated surface area. Faster processing times and greater cut quality are able to result from higher power densities.
The application is going to determine the best laser wave length ultimately. A CO2 laser’s wavelength of 10.6 m is often excellent for cutting and engraving materials like acrylic or wood. Yet, a different wavelength is able to be more beneficial for medical applications like soft tissue surgery. The wavelength that is most appropriate for the job depends on the application’s particular needs.
Do CO2 Lasers emit radiation?
Yes, a CO2 laser emits radiation in a specific spectrum, as with every other laser. The spectral range is found in the infrared region between 9.4 and 10.6 µm wavelengths, depending on the specific gas mixture of a given CO2 laser. The radiation such a laser gives off strongly depends on the spectrum itself. Its laser wavelength is able to be very narrow-banded (i.e., monochrome) or broadband.
What is a CO2 Laser Spectrum?
The laser spectrum defines the emission wavelength of the laser. It is the amplitude of the emitted light as a function of the wavelength. The following figure shows an example of a CO2 laser spectrum:
NOTE: I couldn’t really find a picture showing a CO2 laser spectrum on the web without any copyrights on it. Maybe the company can provide one – I guess, they have plenty of spectra available.
What are the Alternative Wavelengths for a CO2 Laser?
CO2 lasers are able to be tuned by adjusting the gas mixture or the optical components. The most variable parameter is the output power, which is easily altered by changing the pumping power or the position of the outcoupling mirrors or other optical components. Adjusting the wavelength is not easy because the filling gas mixture must be changed, or particular components must be used. A suitable component for CO2 laser tuning is a diffraction grating. This kind of grating is able to be positioned in a way that it selects specific wavelengths, which are then emitted by the laser.
Why are CO2 Lasers used in the Health Industry?
CO2 lasers are widely used in the health sector because they emit infrared light, which is very effectively absorbed by water. Laser radiation is able to cure scars, and wrinkles, remove tissue, or seal blood arteries since the human body is mainly made of water. All these properties make the carbon dioxide laser a perfect tool for dermatology, aesthetics, surgery, or ophthalmology.
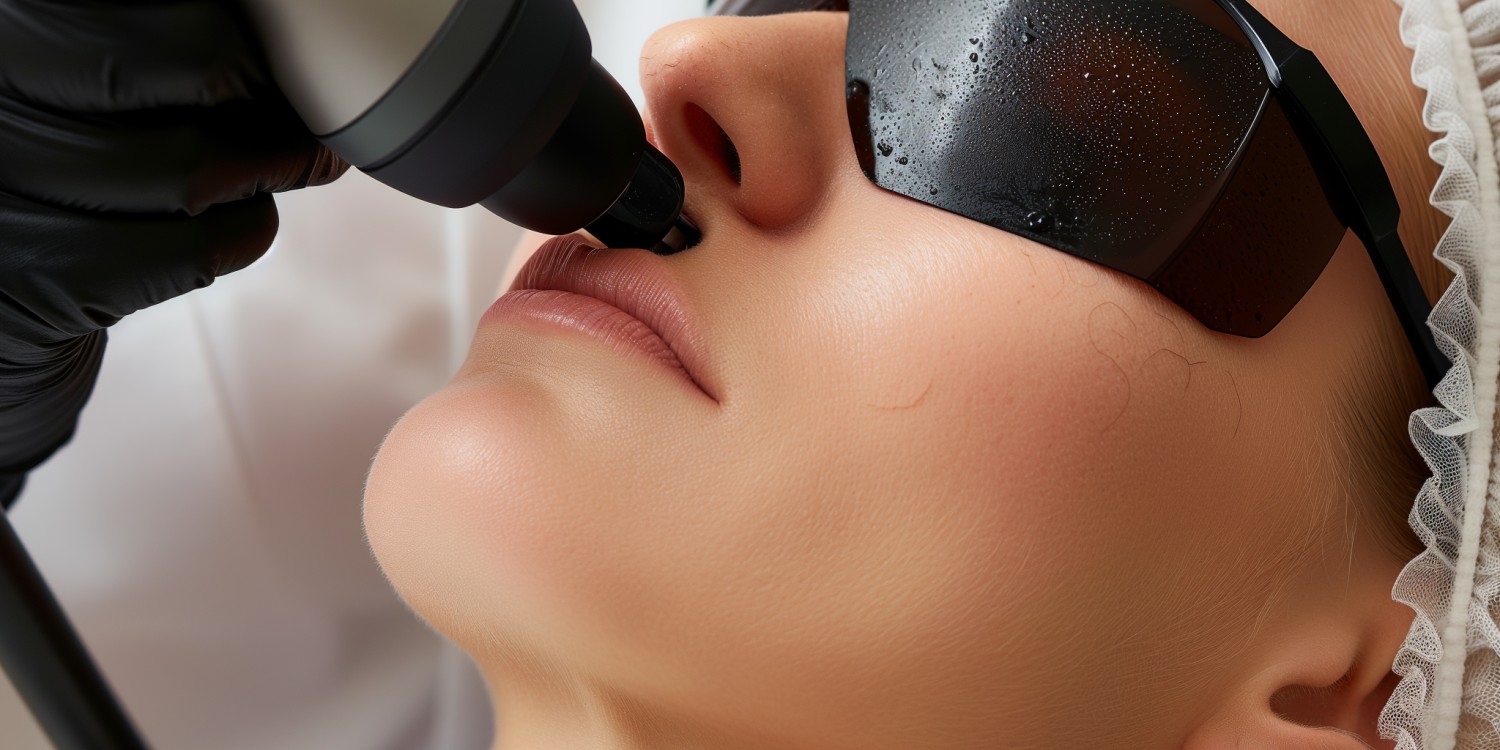
What is CO2 Laser Treatment?
CO2 laser treatment is nowadays mostly found in dermatology. The human skin very well absorbs laser radiation. Thus, it is able to be used to treat different ailments. Examples are the removal of acne scars or spots, wrinkles, or the reparation of skin damage, such as scars. Infrared light from the laser is able to be applied to bleach skin. The usage of CO2 lasers for dermatological procedures was pioneered in the late 1960’ies and early 1970s by scientists like Thomas Polanyi and Geza Jako.
The significant advantages of using infrared lasers in medicine are the short downtime of the laser systems and the long-lasting results they are able to achieve. Furthermore, laser treatment is able to be applied to anybody. There are no allergic reactions or intolerances to laser light, and the pain is minor compared to other surgical procedures.
What are the health benefits of CO2 Lasers?
CO2 lasers offer a broad palette of health benefits, especially when it comes to dermatological treatments. The benefits for the doctor are the reliability and cost-effectiveness of a laser system. Conversely, the patient has a short treatment time with comparable little pain and long-lasting results. Since the laser irradiation is absorbed in a small skin volume, the surgery is precise, and the resulting scars are tiny.
Listed below are the health benefits of CO2 lasers.
- CO2 Laser helps Acne and Acne Scars: A CO2 laser is able to help to decrease acne and acne scars by ablating the top layer of skin and encouraging collagen creation. A CO2 laser resurfacing procedure dramatically reduced acne scarring in 90% of patients, according to research in the Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy.
- CO2 Laser helps for Stretch Marks: The CO2 laser is able to make stretch marks seem better by increasing the creation of collagen and lowering the visibility of scar tissue. Stretch marks’ appearance significantly improved after CO2 laser therapy, according to research published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
- CO2 Laser helps against Melasma: Targeting the skin’s pigmented cells with a CO2 laser is able to help lessen melasma’s appearance. A CO2 laser therapy dramatically reduced melasma in 85% of patients, according to research in the Journal of Cutaneous Laser Treatment.
- CO2 Laser Help for Scar Tissue (Scarring): A CO2 laser is able to assist in minimizing the appearance of scar tissue by ablating the top layer of skin and encouraging collagen formation. The look of scars was significantly improved by CO2 laser resurfacing, according to the Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery research.
- Removes Wrinkles: A CO2 laser is able to help minimize the look of wrinkles by ablating the top layer of skin and encouraging collagen formation. Research published in the Journal of Dermatological Therapy discovered that CO2 laser resurfacing improved wrinkles in 80% of participants.
- Provides Uniform Color: The CO2 laser is able to enhance the look of skin by eradicating pigmentation abnormalities and creating a more uniform color. A CO2 laser therapy significantly improved the texture and abnormalities of the skin, according to research published in the Journal of Cutaneous Laser Treatment.
- Fixes Sking Damages: The CO2 laser is able to assist in treating skin damage by promoting collagen formation and eliminating damaged skin cells. A CO2 laser therapy significantly improved the look of photoaged skin, according to research published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
- Reverse Sun Damage on Skin: The CO2 laser assists in repairing the symptoms of sun exposure by eliminating damaged skin cells and boosting collagen formation. Research published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology discovered that CO2 laser therapy significantly improved the look of photodamaged skin.
- Minimize Downtime: A CO2 laser assists in reducing downtime by ablating the top layer of skin and encouraging speedier healing. Research published in the Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Treatment discovered that CO2 laser resurfacing resulted in a quicker recovery than other laser resurfacing procedures.
- Helps for treating pre-cancerous skin lesions: CO2 laser helps cure pre-cancerous skin lesions by eliminating damaged skin cells and boosting the development of healthy skin cells. Research published in the Journal of Cutaneous Laser Therapy discovered that CO2 laser therapy significantly improved the look of actinic keratoses, a typical pre-cancerous skin lesion.
- Stimulates Collagen for Younger looking skin: A CO2 laser promotes collagen formation, resulting in younger-looking skin. Research published in the Journal of Cutaneous Laser Therapy discovered that CO2 laser therapy significantly increased collagen formation in the skin.
1. CO2 Laser helps Acne and Acne Scars
Momentarily there is a lot of research going on to investigate the effectiveness of CO2 laser treatment of acne and acne scars. One recent study by Ansari et al. found that a fractional CO2 laser is about 14 % more efficient in acne removal than other laser types. Mainly fractional lasers are used to peel off the acne scar tissue.
2. CO2 Laser helps for Stretch Marks
Stretch marks are able to be very unpleasant for the patient. They reduce the aesthetics of the skin and are unable to be easily removed. However, there are a lot of promising research results that show the advantages of treating stretch marks with a CO2 laser. A scientific paper published by Matera et al. in 2020 found a 30 % reduction in stretch mark depth. This figure rises to approximately 45% when paired with other kinds of therapy.
3. CO2 Laser helps against Melasma
Melasma often causes psychological concerns since it shows on a patient’s face. However, this problem is able to be solved with CO2 lasers. The lasers destroy the pigmentation of these dark skin spots. This treatment permanently reduces melasma by up to 50 % after only two treatment sessions. This was very recently demonstrated in a study by El-Sinbawy and his group.
4. CO2 Laser Help for Scar Tissue (Scarring)
Scar tissue is another vital candidate for CO2 laser treatment. Burn scars or scar tissue following invasive surgery, in contrast to acne scars, typically minor scars in vast numbers, are able to create significant complications for patients. It has been shown that fractional CO2 lasers are able to drastically improve the thickness of scar tissue as well as their elasticity. This is a great relief for the patients. The research group of Weihai Peng and his colleagues found in a new study that the side effects of such a treatment are mild and rare.
5. Removes Wrinkles
The light from a CO2 laser penetrates the skin, causing tiny lesions in the top layers. Those micro wounds are harmless but enhance cell growth and collagen production. Consequently, small wrinkles are going to vanish, while larger ones are going to become much smaller. This has been known for quite some time, as this paper by Jeffrey T. Reed from 1997 shows.
6. Provides Uniform Skin Color
Changes in skin color are not only able to be aesthetically problematic. They are able to be a sign of certain illnesses, such as Lichen planus. This is a non-contagious but chronic disease that affects the patient’s hair skin or nails. Certain areas of these body parts are going to exhibit overly pigmented stains, for which there is no proven cure so far. However, in recent years CO2 laser treatment has been reported to reduce or even remove Lichen planus stains. One particular case report by Ramanesh can be found here.
7. Fixes Skin Damages
It is able to be readily seen that a skin treatment with a CO2 laser is able to cure or at least ease quite a wide variety of skin damage. Those are able be wrinkles, burns, acne scars, overly pigmented areas, or stretch marks. There are two significant types of carbon dioxide lasers for dermatological applications: Ablative and fractional CO2 lasers. Both types are used with great success, but the fractional laser is still the most common. The reason is that it removes only parts of the treated area and, thus, keeps unwanted skin damage at bay.
8. Reverse Sun Damage on Skin
Sun damage to the skin is able to manifest itself in various forms. Those range from harmless freckles over melasma and wrinkles to skin cancer. Skin cancer has different forms, either melanoma or non-melanoma (such as Bowen’s disease). The former has been successfully treated with CO2 lasers for quite some time. On the other hand, the latter has been successfully laser treated and exhibited a very low reoccurrence rate, as shown by Sharon et al.
9. Minimize Downtime
CO2 lasers have almost little downtime since they are able to be turned on and off without any preparation. This results in highly cost-effective laser therapy.
10. Helps treat pre-cancerous skin lesions
Treating pre-cancerous melanoma or similar skin lesions is of great importance for the patients. This is because the earlier the treatment starts, the better the results are going to be. The same is true for the chances of successful treatment. The recent study ‘Lasers and Energy-based Devices for treating Pre-cancerous and Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers: A Review of literature’ by Niaz et al. found that CO2 laser treatment is able to decrease the reoccurrence of non-cancerous lesions such as actinic keratosis by 70 to 94 %. Furthermore, the CO2 laser treatment of Porokeratosis, another skin lesion, completely cured the treated patients.
11. Stimulates Collagen for Younger looking skin
Collagen is a very important building block of connective tissue. Thus, a lack of it leads to dents and wrinkles in the skin. Hence, the use of CO2 laser systems in aesthetic surgery or dermatology has become increasingly common. A recent paper by Melissa Morrison Toyos found that fractional CO2 lasers stimulate not only collagen production in the skin in the short term but in the long term. The latter is caused because the laser supports the growth of fibroblasts, which then produce collagen.
What are the possible side effects of CO2 Laser Treatment?
Listed below are the possible side effects of CO2 Laser Treatment.
- Infection: Infection is a danger with any skin therapy, including CO2 laser treatment. The risk of infection is able to be decreased by patients adhering to their doctor’s post-treatment advice.
- Scarring: CO2 laser treatment helps scars look less bad, but there is a chance of getting new scars or making the ones one already has worse. This is more probable if the therapy is given at a high energy level.
- Skin Peeling: CO2 laser therapy is able to cause the top layer of skin in the treated region to peel off. This is a natural component of the healing process and usually goes away after a few days to a week.
- Skin Redness: It is normal to have some redness in the treated region after the treatment. This usually lasts a few days and is treatable with ice packs and over-the-counter pain medicines.
- Milia: Milia are tiny, white lumps that are able to appear on the skin after CO2 laser therapy. They usually go away on their own within a few weeks.
- Changes in Sking Color: CO2 laser therapy is able to induce skin color changes, especially in individuals with darker skin tones. This is more probable if the therapy is given at a high energy level.
1. Infection
There is a risk of infection after every surgical procedure. Microbes such as bacteria or viruses are able to enter the body through the wound. CO2 laser procedures minimize this risk by closing the wound through cauterization. This prevents pathogens from (re)entering the body. The heat produced by the laser beam kills most bacteria and viruses instantaneously. There is, however, a very small risk that some microbes survive the laser treatment and remain in the body or re-enter it through other gaps in the skin. This risk changes depending on the type of procedure. For example, a study published in the journal ‘Dermatologic Surgery’ analyzed over 330 CO2 laser treatments. The authors found that only in 1.1 % of all cases, an infection with the herpes simplex virus occurred.
2. Scarring
Scarring is able to be a problem after CO2 laser treatments, although the danger is minimal if the laser is used properly. An extensive analysis by Hunzeker et al. showed that no scarring occurred from over 2000 treatments with a fractional CO2 laser.
3. Skin Peeling
Skin peeling frequently occurs after any laser treatment, not just when a CO2 laser is used. Usually, this is not a risk but just a natural side effect. A laser heats the uppermost layers of the skin. Therefore, some of the skin cells are going to be dried out, and those are going to peel off quite quickly after the treatment. More skin portions are able to be impacted if the therapy is surgical. The skin is able to peel off after many days or weeks, especially if warts or malignant regions are treated. Some tissue is even able to turn black after specific treatments and develop a crust, just as it would on any other incision. These skin areas must peel off after some more days, and the treated skin area heals afterward.
4. Skin Redness
A slight skin irritation, which leads to tissue redness, is able to be a mild side effect after CO2 laser treatment. The redness is directly caused by the laser energy deposited in the skin or by a reaction to the procedure afterward. It is able to occur, for example, after acne treatment but is generally no reason for concern. The redness commonly peaks on the day of the laser treatment or the day after. It usually vanishes a few days after that.
5. Milia
Milia is as well called milk spots. They are small cysts that form just under the epidermis. They are able to appear after some CO2 laser treatments, but this is quite rare. A paper from 2013 found that only 5 % of the patients experienced milia formation after laser treatments. Ironically, it is very common to treat milia with CO2 lasers.
6. Changes in Skin Color
One of the most occurring changes in skin color due to CO2 laser treatment is hypopigmentation (i.e., a ‘whitening of the skin). This was a notable risk in treatments that used ablative lasers in general. The risk has previously been stated to be more than 50%. The opposite effect of hyperpigmentation is found in around 3 % of laser-treated patients. However, this risk has practically vanished with the advent of non-ablative CO2 lasers. A recent paper found no cases of hypopigmentation in over 2000 treatments with a fractional CO2 laser.
What are the surgeries that CO2 Lasers are used in?
CO2 lasers are used in all kinds of surgeries, from aesthetical surgery over ophthalmology to treating warts, wrinkles, or skin cancer. They are applied in minimally invasive procedures inside the human body. An example of the latter is laser surgery on the larynx or hypopharynx.
Why is CO2 Laser radiation absorbed efficiently in water?
Each material has particular wavelengths of light that it is able to emit or absorb. These wavelengths are virtually the same for CO2 and water. Hence, whatever radiation is emitted from a CO2 laser is swiftly absorbed by water.
Why is cellular vaporization prominent for CO2 Lasers in health?
The water in a cell warms up fast because it absorbs water quickly. This ultimately leads to a rupture of the cell itself. The heat created by the carbon dioxide laser then evaporates the cellular remains. This is the basis for all laser surgery. Thus, it is more accurate to speak of vaporization rather than ‘cutting’ when it comes to laser surgery.
What are the Industrial Uses of CO2 Lasers?
Listed are the industrial uses of CO2 Lasers.
- Laser Welding with CO2 Laser: CO2 laser welding joins metal parts without touching them. The laser beam burns metal at the junction, which forms a strong connection. Stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium are welded using CO2 lasers. CO2 laser welding is accurate, rapid, and distortion-free due to its high energy density.
- Laser Cutting with CO2 Laser: High-powered CO2 lasers cut metals, polymers, and wood in CO2 laser cutting. The laser beam vaporizes the material, generating a narrow kerf with little waste. Thin metal sheets, intricate geometries, and sensitive materials are often cut using CO2 lasers.
1. Laser Welding with CO2 Lasers
Laser welding occurs because the workpiece material absorbs the radiation from the laser. Only the top layers absorb light at power densities up to 100 W/cm2. Hence, the laser beam does not penetrate far into the material. This method is called conduction limited welding. This means that the speed of the process is determined by the heat conduction within the material itself. One speaks of keyhole welding if the power densities are above the aforementioned threshold. The workpiece material is molten and evaporated at such high laser strengths, and the highly concentrated laser beam functions like a drill. The first case leads to shallow cutting over quite a large area. The second one is used for welding thick pieces very precisely.
2. Laser Cutting with CO2 Lasers
Laser cutting applies, in principle, the exact mechanisms as keyhole laser welding. The difference is that the laser power is even higher (several kW and more per cm²). At such high power, the material is nearly immediately evaporated. Sometimes a gas flow is involved to blow the vapors quickly away. This enables very precise and yet rapid laser cutting of all kinds of materials, from metals to ceramics.
What are CO2 Laser Cutters?
CO2 laser cutters are laser cutters in which the laser radiation comes from a carbon dioxide laser. This type of laser cutter is usually adjustable, affordable, and robust. The output power of a CO2 laser cutter varies depending on the application. The power is commonly adjustable. Thus, a large variety of materials of different sizes and shapes are able to be cut rapidly and precisely. Laser cutters are able to cut plates, rods, or workpieces with more complicated 3D shapes.
There are numerous CO2 laser cutters Glowforfe Pro, Epilog Laser Zing 24, and Boss LS-1416. Ultimately, the best CO2 laser cutters that suit one are going to be determined by their individual requirements, budget, and degree of experience. It is essential to study and evaluate several models before making a purchase to ensure that one receives the correct equipment for the requirements.
Are CO2 Lasers used in the Automobile Industry?
Yes, CO2 lasers are widely used in the automotive industry. Their ability to effectively weld or cut materials and workpieces with complex shapes makes them a working horse for automobile manufacturing. Other advantages are their high output power and their robustness. These factors enable short downtimes and superior cost-effectiveness.
Are CO2 Lasers used in the Aircraft Industry?
Yes, CO2 lasers are used in Aircraft Industry. The lasers are used for the same purposes: cutting and welding complex parts with high precision and rapid speed. Their precision makes them very interesting for aerospace manufacturers because their high-tech parts need the most accurate fabrication.
Are CO2 Lasers used in the Jewelry Industry?
Yes, CO2 lasers are used in the jewelry industry. CO2 lasers are able to precisely cut or engrave lots of materials, such as noble metals. Hence, they are widely used by designers of jewelry. A CO2 laser system is able to be used on fragile or delicate objects and cut them with extreme precision. It allows jewelers to expand the limits of what is able to be made from gold, silver, or platinum. A laser cutting system is able to replace many highly expensive tools or other equipment for an affordable price.
Are CO2 Lasers used in the Textile Industry?
Yes, the textile industry makes heavy use of CO2 laser cutting. It is commonly used either to cut cloth or engrave it. Laser-engraved fabrics look very neat and are able to be used for merchandise. The engravings are very endurable and have to be manufactured in large quantities. This is where rapid laser cutting and engraving come into play.
What is the difference between CO2 Lasers and Fiber Lasers?
CO2 lasers employ a gaseous laser medium, while fiber lasers use optical fiber. This fiber must be doped with rare earth materials to become laser active. Another difference between CO2 Laser vs. Fiber Laser is the typical wavelength of laser radiation. Fiber lasers have substantially shorter wavelengths than CO2 lasers, which have an emission range of 9.4 to 10.6 m. The latter typically emit beams with wavelengths between 700 nm and 2200 nm. The kinds of materials each laser is able to treat vary substantially along the wavelength range. The laser type is going to be selected based on the cut, engraved, or welded material. Generally, a CO2 laser cutter is usually faster than a fiber laser cutter.