Our Latest Posts

Anodized Aluminum: Definition, History, Importance, Types, and Stages
Anodizing is a technique to artificially increase the thickness of an oxide layer on a certain material. Normally, only metal surfaces are able to be anodized. The reason for this is that the workpiece that must be anodized has to be used as the anode in an electrolytic process. Hence, the name ‘anodization’. Another major advantage is the fact that anodic layers adhere to surfaces very well. However, these layers are relatively brittle compared to other forms of coatings. They have very good mechanical stability but are somehow sensitive to thermal stress. One of the most important materials for anodization is aluminum. Anodized surfaces have superior wear and corrosion resistance. They provide excellent adhesion for glues and paints. Anodizing aluminum was first employed on an industrial level in 1923, to add a corrosion protection layer to airplanes. This process utilized chromic acid but patents with other acids, like oxalic acid,

How to Laser Engrave and Cut Cork
Cork is a natural material that is made from the bark of cork oak. It is used for many purposes. For example, it is able to be applied for sealing wine or Champaign bottles, or to make handbags, or wallets. Laser-cutting cork generates very fancy-looking items for design and decoration purposes. Cork has excellent contrast and is therefore perfectly suited for laser cutting or engraving. The best laser system for cork is a CO2 laser such as the LS series from Boss Laser. The optimum power, speed, focal length, and airflow level are strongly dependent on the thickness of the cork plate that must be cut or engraved. Cork is able to be cut or engraved with relatively minimal input power because of its great contrast. Here is what must be done to get the best results: How to Laser Cut and Engrave Extruded Cork? Listed below are the six

How to Laser Engrave and Cut Delrin
Delrin is a brand name for a class of polymers. It is the class of polyoxymethylene (POM). POM has a number of preferable properties, such as high wear resistance and excellent electrical properties. It is able to easily be cut and engraved with a laser since it is a thermoplastic. A suitable laser system like a CO2 or a fiber laser melts or evaporates the Delrin quickly and precisely. Thus, a focused laser beam is optimal for laser cutting and engraving of Delrin sheets or plates. Here is what must be done to get the best results: How to Laser Cut and Engrave Extruded Delrin? Listed below are the eight steps on how to laser cut and engrave extruded Delrin. How to Laser Cut and Engrave Cast Delrin? Listed below are eight steps on how to laser cut and engrave cast Delrin. What are the differences between General Part and

What is Glass? Definition, Types & Uses
Glass is a solid, non-crystalline substance that is often created by melting silica or other minerals at high temperatures and then fast cooling it to avoid crystallisation. It is distinguished by its transparency, hardness, and chemical and heat resistance. Glass has been used by humans for thousands of years. The first ones to manufacture glass were the ancient Egyptians at around 1500 BC. The range of conceivable uses for glass has broadened considerably since those times. Glass is used a lot in constructing, packaging, electronics, transportation, art, and scientific equipment because of its unique properties. It is able to be produced in a range of hues, patterns, and forms to accommodate various needs. Moreover, there are various types of glass, including stained glass, lead glass, borosilicate glass, soda-lime glass, aluminosilicate glass, and silica glass. What is Glass? Glass refers to a solid material that is commonly used in a wide
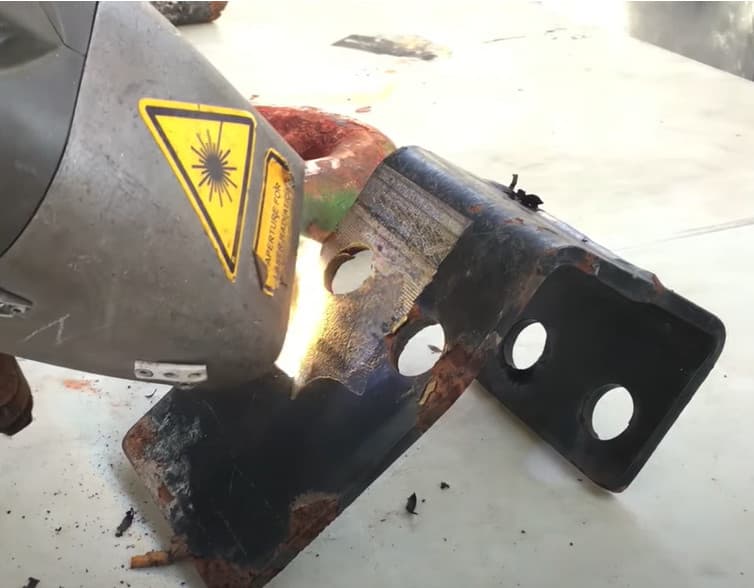

Laser Ablation: Definitions, How it Works, Applications, and Parameters
Laser ablation (or laser-blasting, as it is sometimes called) describes the removal of the top surface layers of a material. Mostly, laser ablation is done on solid surfaces, but, in principle, liquids are able to be laser blasted as well. The removal works as follows: a high-energy laser beam is directed onto the material, where it heats the surface rapidly. It is commonly done with a pulsed laser in the nanosecond regime. The laser light’s energy is quickly absorbed by the material, which, in turn, evaporates or even sublimates. Usually, UV lasers are used for laser ablation because they have a relatively short wavelength (i. e. about 200 nm). Shorter wavelengths correspond to higher beam energy, which helps with the laser ablation process. The possibility of unintended extra surface damage must be considered since the material is heating up extremely quickly. However, such damage is able to be minimized by
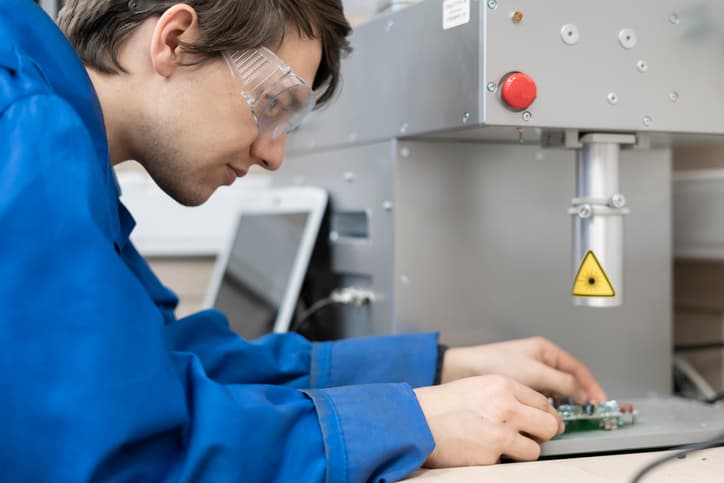

Laser Fracture-Controlled Cutting: Definition, Process, and Laser Type
Laser fracture-controlled cutting is a process that uses a laser beam to fracture a material in a controlled manner. The method is often used in the aerospace and automotive industries to cut materials such as titanium, stainless steel, and aluminum. The process is highly accurate and is able to produce smooth edges with minimal distortion. The process of laser fracture-controlled cutting involves a high-power laser beam being directed at the material, creating a small kerf, or cut. The laser then fractures the material along the kerf, causing it to break cleanly. The cut is completed by a mechanical process, such as a punch or a water jet, which pushes the material out of the way. The laser type used in fracture-controlled cutting depends on the material being cut. For example, a CO2 laser is able to cut thick steel, while an Nd:YAG laser is well suited for cutting aluminum and
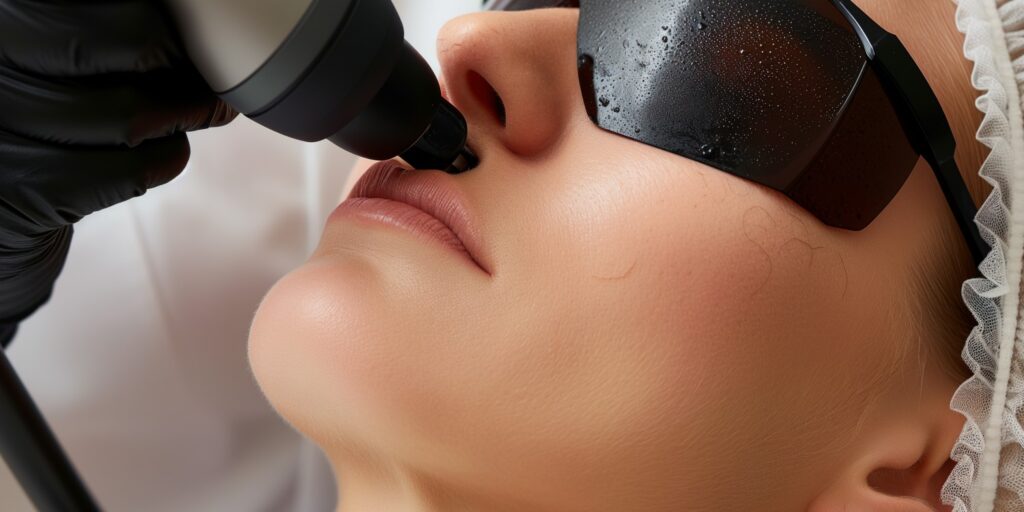
What is a CO2 Laser? Carbon Dioxide Laser Resurfacing
A CO2 laser is a type of gas laser. It is very robust and reliable and relatively easy to build. It was really among the earliest kinds of lasers to be constructed in 1964. The laser medium for this type of laser usually consists of a mixture of CO2, nitrogen, and helium. CO2 lasers belong to the class of high-power lasers. The radiation that is emitted by such lasers lies between 9.4 and 10.6 µm. They are able to reach output powers of tens of kW and output energies of up to 100 J. They are widely used in a variety of sectors since they are able to provide such high outputs. CO2 lasers of up to 200 W of output power are typically used for laser cutting and engraving of various materials, including plastics and wood. Pulsed lasers with up to 6 kW output power are used for cutting

How to Laser Engrave and Cut Acrylic (Extruded and Cast)
Laser cutting is a highly sophisticated method of cutting materials very precisely. Another option is laser engraving, which uses quite similar equipment. Both methods are based on CAD files, which contain the outline of the shapes that have to be cut. A powerful laser system then cuts or engraves the desired patterns. It does that by melting or vaporizing the workpiece material. One particularly interesting material for laser cutting, or engraving, is acrylic. Most commonly, this polymer comes in acrylic sheets, such as Plexiglas. However, acrylic is usually used to describe a whole class of materials rather than just Plexiglas. The most popular lasers for cutting or engraving acrylic are CO2 lasers. They usually have output powers between some dozen to some hundred watts. The choice of output power depends on the thickness of the acrylic. The speed of such laser systems starts at around one mm/s and is able
How to Laser Engrave and Cut Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate (PC) is a very versatile material. It is a thermoplastic polymer with good mechanical properties and durability. It is sometimes called Lexan, Hyzod, Makrolon, or Tekanat. Those are all brand names for the same material. Laser cutting polycarbonate is able to be easily done with a 10.6 µm CO2 laser cutter. However, one has to be aware that the laser beam is able to discolor the PC sheet. Generally, the thinner the sheet is, the better the results are. For laser engraving of PC, a fiber laser is the best choice. It must have the same wavelength as the CO2 laser cutter (1064 nm). The fiber laser is going to leave black markings on the PC if done correctly. These markings are permanent and have excellent contrast. For example, a very suitable laser system for laser cutting of PC is the LS series from Boss Laser. The optimum power,

11 Best Plastic for Laser Cutting
Plastics is one of the most common materials for laser cutting. It is due to its distinctive qualities like lightweight, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Many different forms of plastics are available for laser cutting, and each has its special features and advantages. Generally, a laser cuts plastics by melting or evaporating them. It is able to be done with high precision and speed, depending on the type of laser and the type of plastics. There are other aspects to be taken into account. For example, the thickness of the plastic sheets or the type of laser cutter that must be used is important. There are three main types of laser cutting systems: CO2, fiber, and solid-state lasers like the Nd:YAG. Listed below are the best plastic for laser cutting. 1. Styrene Styrene or polystyrene (PS) is a kind of vinyl polymer. It is able to be molded under elevated





